
-

HIGHLIGHTS
Franciscus Sylvius and his pupil Reinier de Graaf transformed iatrochemistry from a speculative medical theory into a clinically grounded and
Medieval physicians interpreted the brain through uroscopy, tracing a diagnostic reasoning that linked urine, humoral imbalance, and cerebral function. This
Focusing on Philoponus's commentary on Aristotle’s "Physics", this lecture will examine the recovery of the Greek text and its later
Sharhzad Irannejed examines medieval Islamicate diagrams of the brain and its ventricles as variable scribal artefacts, arguing that their visual
What are occult qualities, and why did they become a central problem in Renaissance natural philosophy and medicine? This lecture
in this talk, Brooke Holmes presents the history of the ancient concept of "sympatheia", from the emergence of the language
LATEST PUBLICATIONS
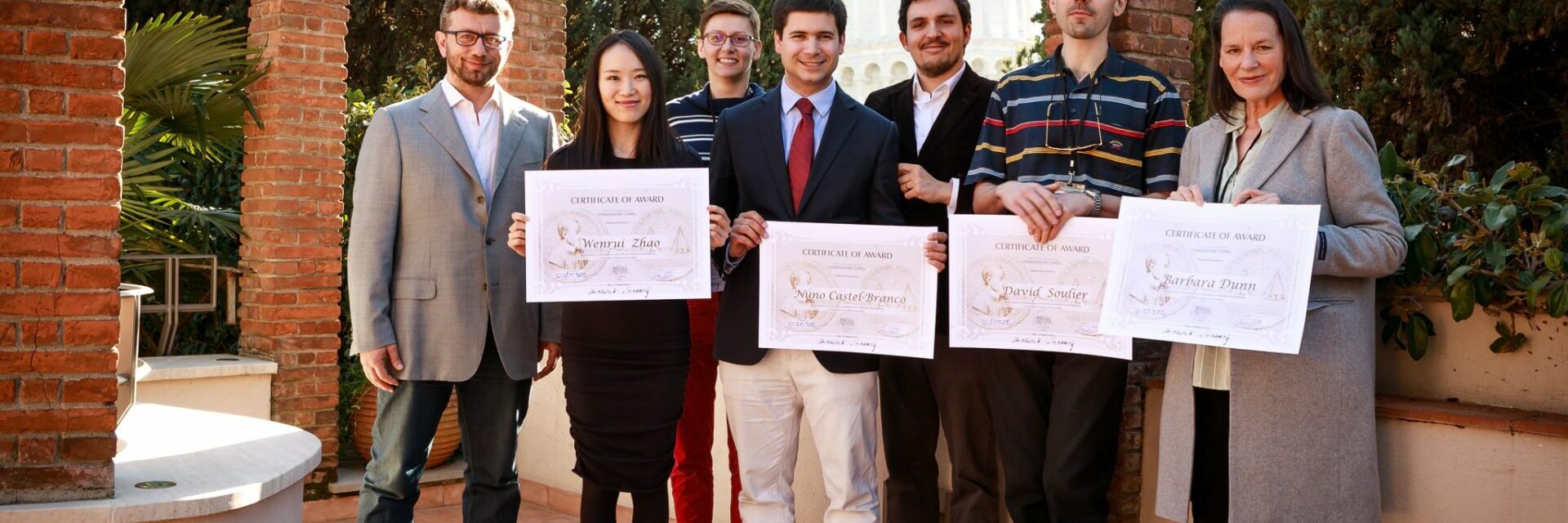
OPEN GRANTS
-

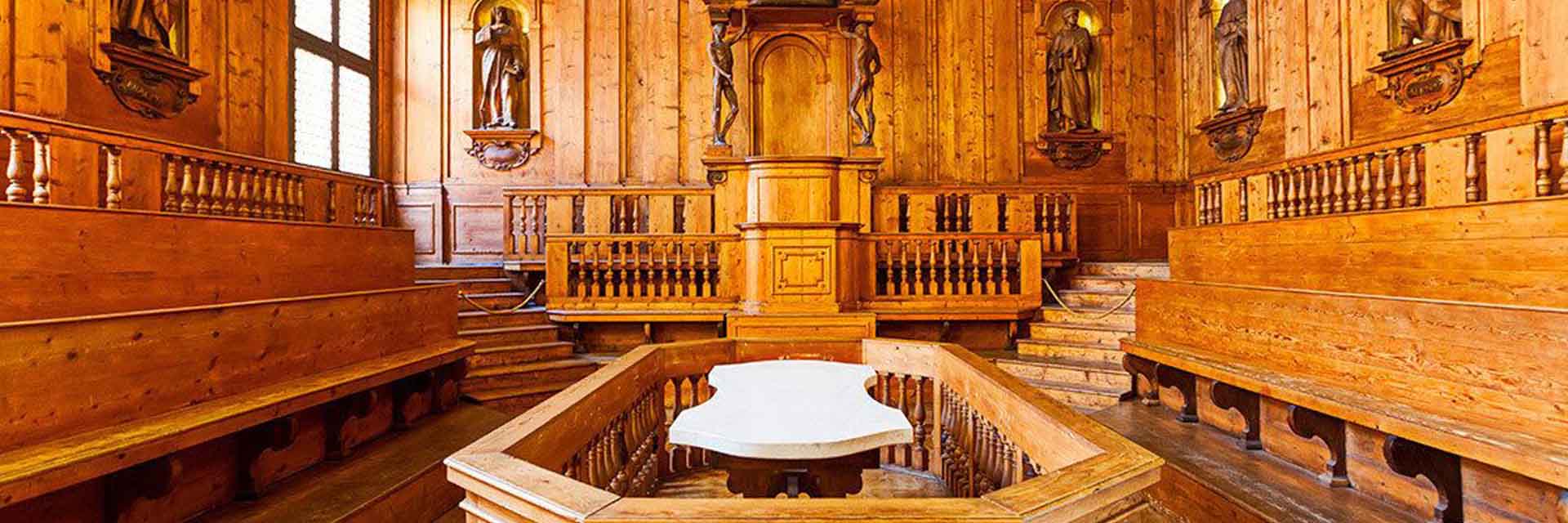
WINTER SCHOOL 2026
Studiolo Digital Humanities Lab is a new format for the Winter School, designed to meet the needs of those who,
-

FORMA FLUENS
Franciscus Sylvius and his pupil Reinier de Graaf transformed iatrochemistry from a speculative medical theory into a clinically grounded and
Medieval physicians interpreted the brain through uroscopy, tracing a diagnostic reasoning that linked urine, humoral imbalance, and cerebral function. This
“Dell’Elettricismo” (1746) was the first Italian treatise to systematically connect electricity with physiology and medical practice. By analysing its experiments
How were miners affected by their work? This article traces the illnesses they faced, the vocabulary they created to describe
Paul Sandro Heidelbach explores a 1688 satire that linked Kenelm Digby’s "sympathetic powder" to a supposed method for finding longitude
In this article Sabrina Engert examines how Andreas Vesalius’s "De humani corporis fabrica" and "Epitome" were re-edited, adapted, and transformed
-

MEDIA GALLERY






































 Visit Our YouTube Channel
Visit Our YouTube Channel